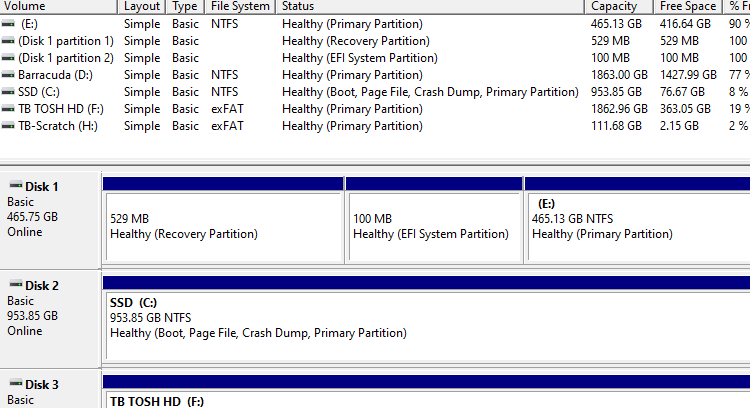
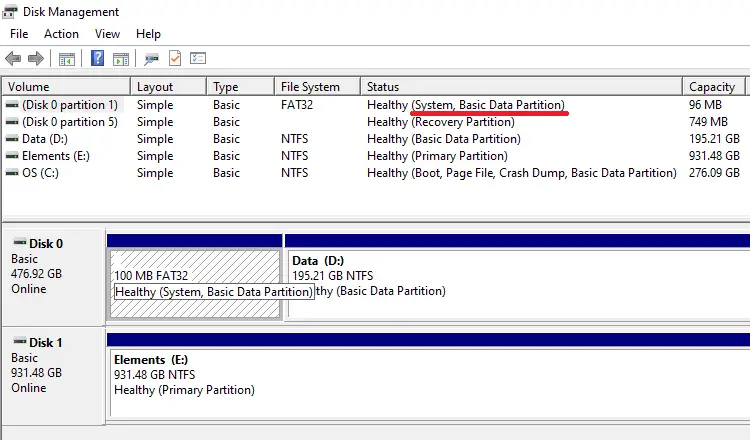
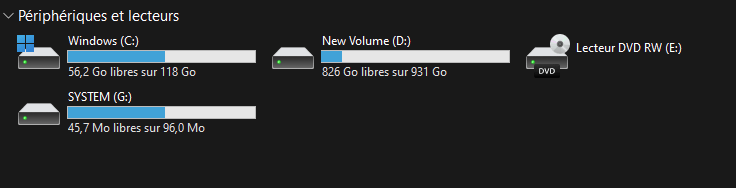
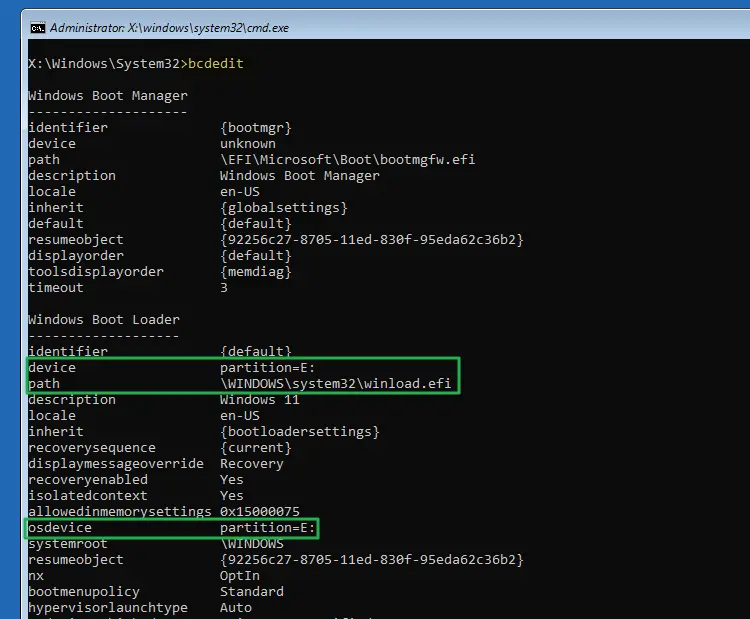
The EFI partition is created automatically when you install Windows. However, after adding a second HDD/SSD and installing Windows on that disk, you may realize that the EFI system partition remains on the old hard disk. You wonder how to move the EFI partition from the old hard drive to the new one.Read more
diskpart
How to Fix the EFI Boot Partition’s ID Using DiskPart
Each partition type is strictly identified by a GUID number. For example, the data partitions (“Basic data partition”) are identified by the GUID ebd0a0a2-b9e5-4433-87c0-68b6b72699c7. The EFI partition has the GUID c12a7328-f81f-11d2-ba4b-00a0c93ec93b.
However, on some systems, the EFI partition may have an incorrect ID assigned for unknown reasons. As a result, the EFI partition may appear as a “basic data partition” when you open Disk Management.Read more
Why is “Extend Volume” Grayed out in Disk Management
When you try to extend a volume in Disk Management, the Extend Volume option may be grayed out even though there is unallocated space on the disk.Read more
[Fix] EFI System Partition Appears in Explorer
The EFI system partition, which contains your boot files and boot configuration database, is hidden by default. However, on some systems, the EFI partition may show up with a drive letter in File Explorer.
How to Find if a Disk Uses MBR or GPT
Knowing how your disks were set up (MBR vs. GPT) is essential for troubleshooting boot issues and Windows Update errors. Master Boot Record (MBR) disks use the standard BIOS partition table. GUID partition table (GPT) disks use the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI).Read more
How to Rebuild the EFI Boot Partition, BCD and Boot Files
The EFI boot partition is a FAT32 partition that stores the boot files and the boot configuration data (BCD) to load Windows. Sometimes, the boot partition or the BCD may get corrupted, and the boot files remain unserviceable by the Windows Setup process. In that case, rebuilding the EFI partition and recreating the BCD & boot files should resolve the issue.Read more