The Windows Update channel delivers all necessary updates suitable for your system. Most of the time, manual intervention is not required for installing updates. In some cases, especially during manual installation of an update using standalone installer, you may need to first check if a specific update (a prerequisite update) is installed on your system.
This article explains how to check if a specific Windows Update (KBnnnnnn) is installed in your computer or not.
Find if a Windows Update KB has been applied
- Method 1: Check the Windows Update history
- Method 2: View installed updates in Programs and Features Control Panel
- Method 3: Use DISM command-line
- Method 4: Run the KB update installer (.msu) file again to test
- Method 5: Using WinUpdatesList utility from NirSoft
- Method 6: Using WMI command-line tool
- Method 7: Check the Windows Update CBS Registry Entries
How to Check if a Windows Update (KB) is Installed on your Computer
There are at least seven different methods to determine if an update is installed in the system.
Method 1: Check the Windows Update history
The modern Settings app has an option to view Windows update history. Here’s how to view it.
- Open Settings and click Update & Security
- Click View update history. The update history page shows the list of updates installed on your computer.
- Scroll through the list and find the specific update (
KBnnnnnn) you’re looking for.
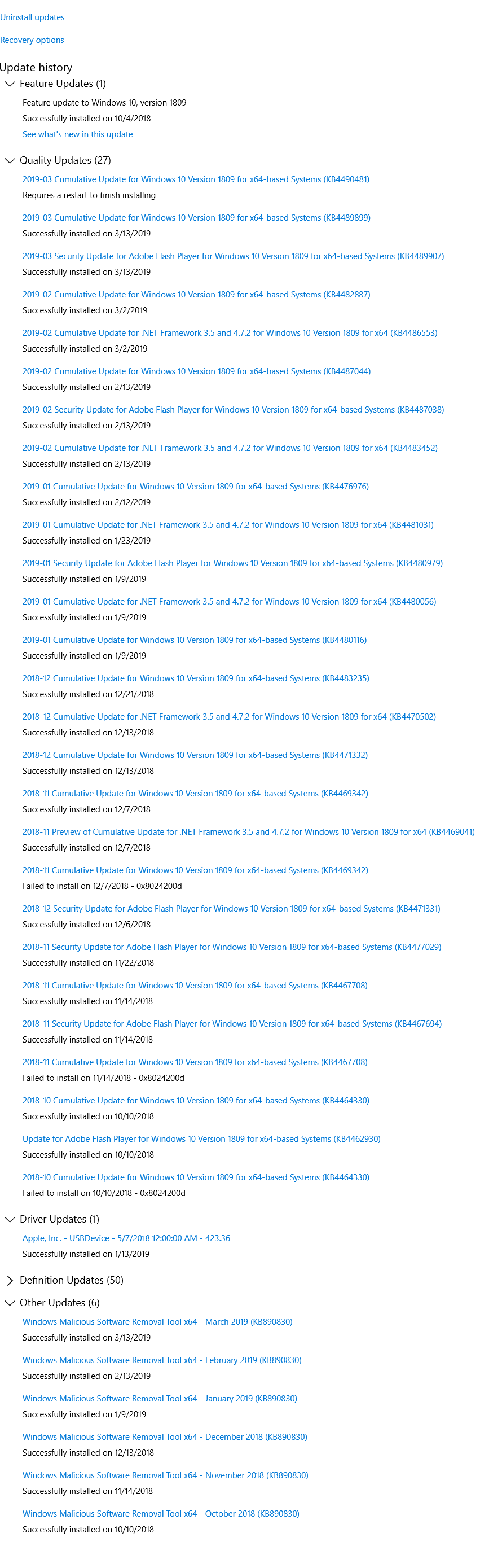
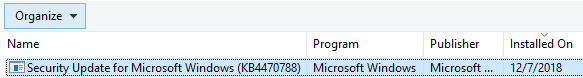
Editor’s note: The update history page may fail to show some updates. In my computer, the update the Servicing Stack Update (SSU) KB4470788 was not listed in the update history page even though the update was installed a few months back.
Method 2: View installed updates in Programs and Features Control Panel
Using the “Programs and Features” applet in the Control Panel, you can find the list of installed updates.
- Right-click Start, click Run.
- Type
appwiz.cpland click OK. This opens the Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel. - Click
View installed updateslink in the left side. This shows you the list of updates along with the installation date column.
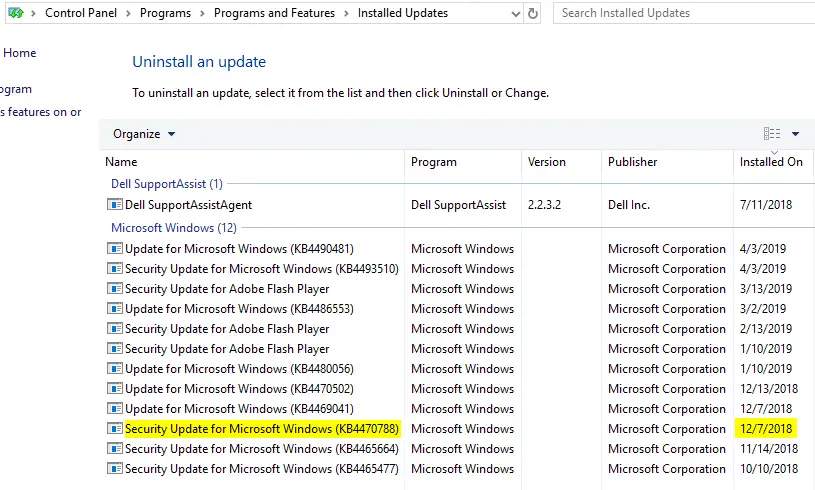
Note: In the classic Programs and Features applet, the Servicing Stack Update (SSU) KB4470788 is listed, and the install date showing up as Dec 07, 2018. It appears that the “View update history” option in the modern Settings app and “Programs and Features” are using two different sources for finding the update history.
Method 3: Using DISM command
The built-in DISM tool can list out the installed Windows Update CBS packages. Follow these steps:
- Open an administrator Command Prompt window.
- Type the following command and press ENTER:
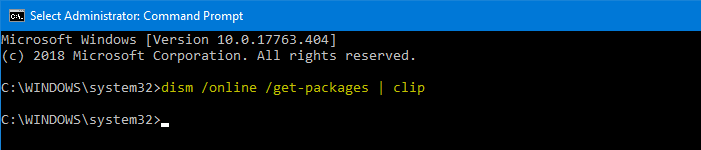
dism /online /get-packages | clip
- Open Notepad and paste the contents from clipboard (Ctrl + V)
- Use the
Findoption in Notepad to check if the updateKB4470788is installed.
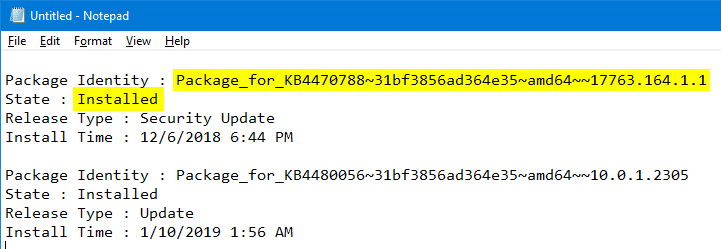
Note: The update Install Time shown by DISM may be in GMT.
The output is redirected to clipboard (using | clip operator).
Method 4: Run the KB update installer (.msu) file again.
Running the KB setup .msu again will tell you if the update has been already installed. Here is how to obtain the standalone installer from Microsoft Update Catalog and run the .msu setup file. Note that this method works for Windows update standalone installers .msu only. That is, this method doesn’t apply if you have the .cab version.
- Visit the Windows Update Catalog
- Download the update package (
.msu) by mentioning the KB number. - Double-click the
.msufile to run the setup. The Windows Update Standalone Installer (WUSA) searches for updates on your computer and determines if the update is already installed or not.
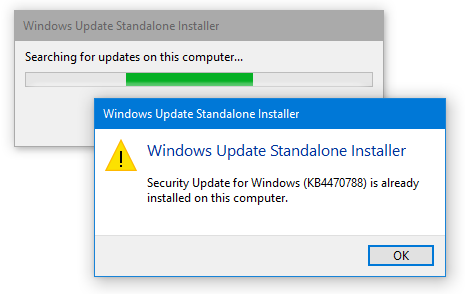
If it’s already installed, it shows the message saying “(KBnnnnnn) is already installed on this computer.”
Method 5: Using WinUpdatesList or WinUpdatesView utility from NirSoft
The WinUpdatesList utility (wul.exe) from Nirsoft displays the list of all Windows updates, including Service Packs and Hotfixes installed on your local computer. You can copy the list of updates to the clipboard, or save it to text/HTML/XML file in a single click. The following fields are shown for each update listed. We’ve covered WinUpdatesList in the article How to Print Your Windows Update History By Exporting to Text or HTML File?.
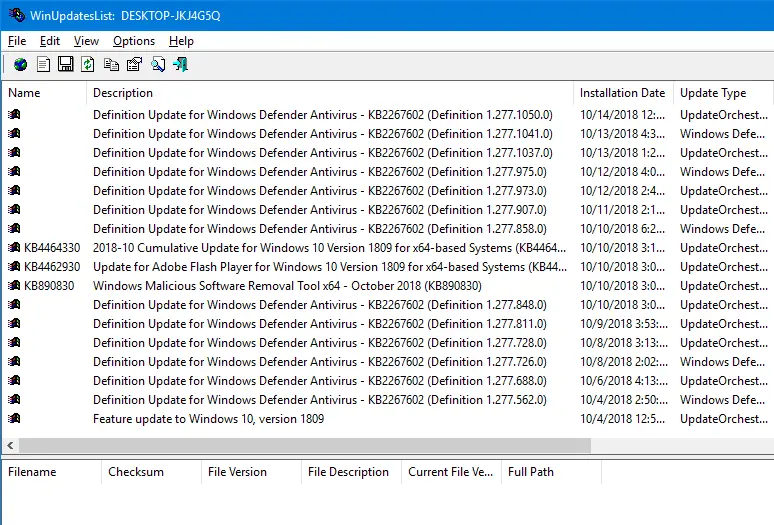
Note: The WinUpdatesList utility, however, did not list the Servicing Stack Update KB4470788 on my computer. Hope this tool works well in your case.
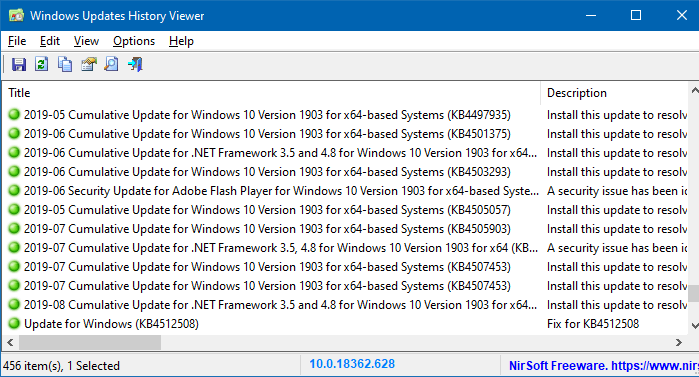
WinUpdatesView (Windows Updates History Viewer)
WinUpdatesView is a simple tool from Nirsoft that displays the history of Windows updates on your system. WinUpdatesView can load the Windows updates history from your local system, using API, and it can also read and parse the Windows updates database file (DataStore.edb) from an external drive or from a remote computer on your network.
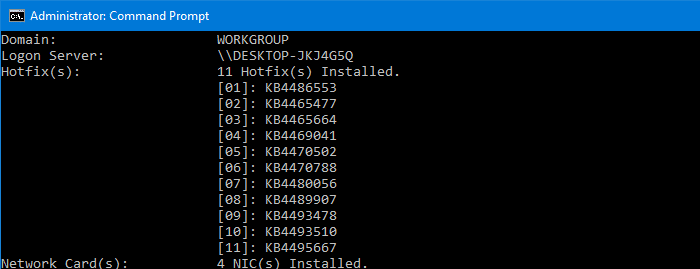
Method 6: Using WMI command-line
From an admin Command Prompt, run:
wmic qfe list full /format:table
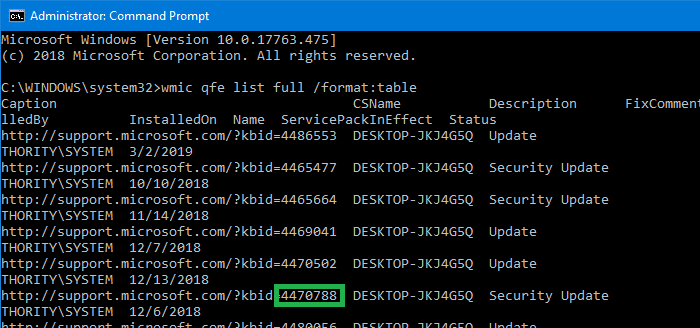
It shows the list of updates installed along with the date of installation and other details.
Or Export to HTML file, using this syntax:
wmic qfe list full /format:htable >D:\hotfixes.htm
Or to list a specific update, run:
wmic qfe list full /format:table | findstr /i "4470788"
Alternately, you can run the command Get-Hotfix from a PowerShell window to get the same results.
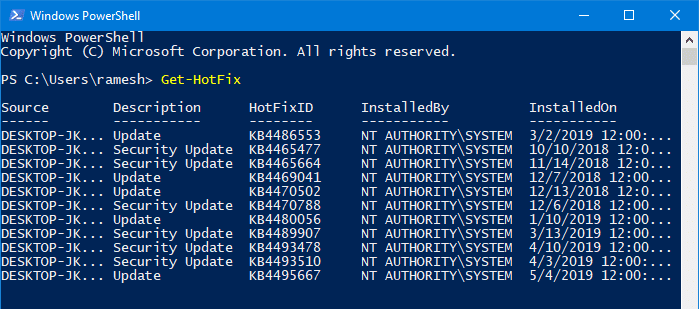
You can sort the table by the InstalledOn column in descending order by running this command:
Get-HotFix | Sort-Object InstalledOn -Descending
PowerShell’s Get-HotFix cmdlet also uses the WMI’s Win32_QuickFixEngineering (QFE) class as the WMIC CLI tool above. The output is exactly the same.
The systeminfo command from a Command Prompt window also lists the hotfixes installed. It again uses the WMI QFE class to query the list of hotfixes.
Method 7: Check the Windows Update CBS Registry Entries
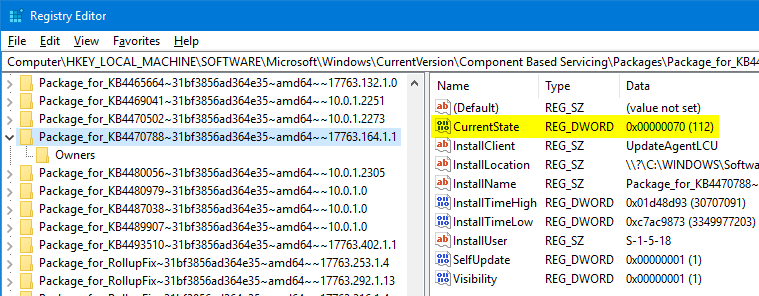
For each update installed, a corresponding Component Based Servicing package registry entry is created. Using the Registry Editor, you can check whether a Windows update has been installed on your computer.
- Start the Registry Editor (
regedit.exe) - Go to the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Component Based Servicing\Packages
- Use the Find option under the Edit menu, and search for the key having the text
4470788(to findKB4470788related entries.)If the key exists, you’re taken to the branch. In my case, as the update was already installed, the Find option led me to this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Component Based Servicing\Packages\Package_1_for_KB4470788~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~17763.164.1.1
- In the right-pane, check the value data for “CurrentState”. If the value data reads
0x00000070 (112), it means that the update was successfully installed.
Here is the list of possible
CurrentStateregistry values and their meaning:Applicable/Current State Hex Dec Absent 0 0 Uninstall Pending 0x5 5 Resolving 0x10 16 Resolved 0x20 32 Staging 0x30 48 Staged 0x40 64 Superseded 0x50 80 Install Pending 0x60 96 Partially Installed 0x65 101 Installed 0x70 112 Permanent 0x80 128 Source: CBS Servicing States Chart – Refresher – Tip of the Day

Determine the install date & time of an update using registry
Each CBS Package key has two values namely
InstallTimeLow&InstallTimeHigh. These keys, when decoded will show you the date and time the update was installed. However, we have a shortcut way to find the exact installation date and time the update was installed on your computer.The trick is to export the Package branch to a
.txtfile (instead of.regformat) and read the timestamp mentioned in the file. We’ll find the installation date and time of updateKB4470788in this example.- In the Registry Editor, select the following (
KB4470788) key:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Component Based Servicing\Packages\Package_1_for_KB4470788~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~17763.164.1.1
- Right-click on the package key and click Export.
- In this example, we’ll export the
Package_1_for_KB4470788~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~17763.164.1.1branch. - In the Save as type: choose “Text files (*.txt)”.
- Give a name for the exported file and click Save.
- Open the .txt file and see the “Last Write Time:” data.
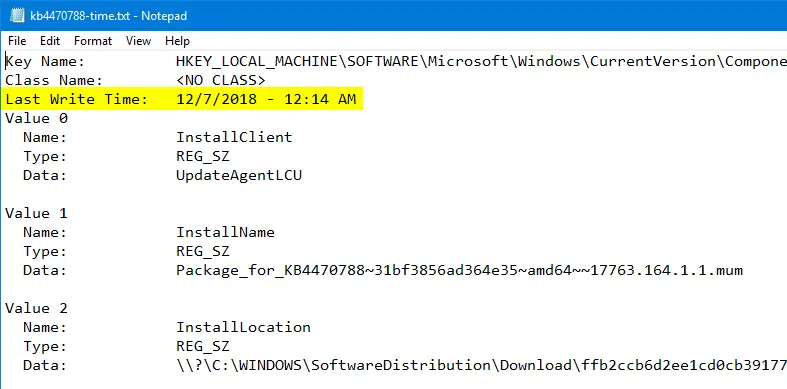
The last write time denotes the date and time the registry entry was created.
As you can see, the last write time in this example matches with the date and time we determined in
Method 2using “Programs and Features”.
- In the Registry Editor, select the following (
That’s it! Hope this article helped you check if a specific Windows Update (KBnnnnnn) has been applied to your system or not.
One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
One "tiny" share from you would seriously help a lot with the growth of this blog. Some great suggestions:- Pin it!
- Share it to your favorite blog + Facebook, Reddit
- Tweet it!
Related articles
- How to Install CAB and MSU Updates from Windows Update Catalog?
- Directly Download Updates From Microsoft Update Catalog Using Any Browser
- How to Print Your Windows Update History By Exporting to Text or HTML File?
Today is Monday May 4 2020
Thank you Ramesh Srinivasan for such a wonderfully detailed Windows Update Cataloged installed KB events on windows OS .
Mine is OS 8.1.
I always used my Windows “Installed Updates” “Review Your Installed Updates”
window requests, however a specific request windows was missing in the window updates OS 8.1 manager. “Search for An Installed Update. All I had to do was put in the KB, this one I am looking for is the Cumulative OS8.1 KB2919355
If the search for a single update window was there, all I would have had to do is put in the KB and it would be searched , singled out and displayed if installed.
Then I would have never found your marvelous Windows Update Article on how to check if a Windows Update is installed.
An “end User” I am, I love entering those CMD’s in the Administrator CMD, and Powershell commands.
Thank you for an easy to understand white paper on it , fit for any End User to Proficient Cheers on that.
OK, in the event that a KB is re-released in the same month, how can you tell by reviewing which “version” of the KB (probably by internal date) is installed?
Hi Ramesh,
We are facing issue with Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Datacenter server we are unable to install the windows updates through check for updates. when we are tried to install the download patch from catalog getting an error “The Update is not applicable to your computer”. we are not able to see any update hostory as mentioned above except the Registry path.the last installed update is june_2021 patch. We also unable to install the latest SSU.