When you search for files on your computer using Windows Search via File Explorer or Cortana, the files you expect to find may not appear in the search results. This happens even though the files exist on the computer.
Another situation is that some phantom files appear in search results, whereas you may have deleted the files long back. In some cases, the searches may be very slow whether or not the folder location is included in the index.
This post tells you how to fix Windows Search issues in Windows 10 and earlier.
Reset and Rebuild the Search Index
Cause
The above-mentioned issues usually happen if the search index hasn’t updated correctly. Here are the possible causes of the problem:
- Windows Search service fails, with error
0x80070002or0x80070005. - Windows Search service fails, with error
0x80040d06(-2147749126) indicating that the catalog is corrupt. In this case, a complete reset ought to fix the problem. - The file is not in an indexed location, so searches may run slow.
- The file type of the file you’re trying to find is not indexed.
- The file has properties that prevent it from being indexed.
- The file has no index attribute that prevents it from being indexed.
- The search indexer has not updated the file in its database.
- Search may be slow due to the huge
Windows.edbdatabase
As Windows Search indexes the details and meta information of every file from included locations, your search queries fetch results quickly. This is because Windows Search fetches results from its database file (.edb) rather than searching the file system. When searching non-indexed locations, searches will be accurate but very slow as the system has to scour through every file and folder.
Windows Search and the advanced query syntax are awesome features when they work, and indexing is one of the best features Microsoft has added to Windows.
How to Repair, Reset and Rebuild the Windows Search Index
Using Search Troubleshooter
Most of the Search Indexing issues can be fixed using the built-in Windows Search Troubleshooter tool.
- To run the search troubleshooter, right-click Start, click Run. Type the following command and click OK.
msdt.exe -ep SystemSettings_Troubleshoot_L2 -id SearchDiagnostic
In Windows 10, you can also launch the troubleshooter via Start → Settings → Update & Security → Troubleshoot → Search and Indexing
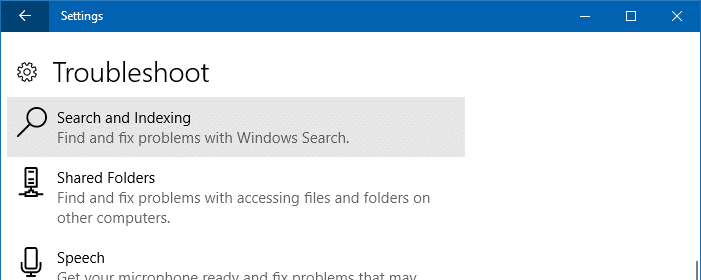
- In the troubleshooter window, click Advanced and select Apply repairs automatically if you want the tool to automatically fix your settings. If you just want to do a dry run, have the option unchecked.
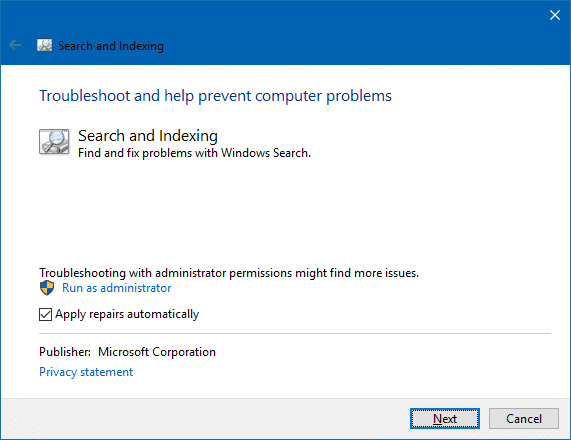
- Select all the checkboxes that apply.
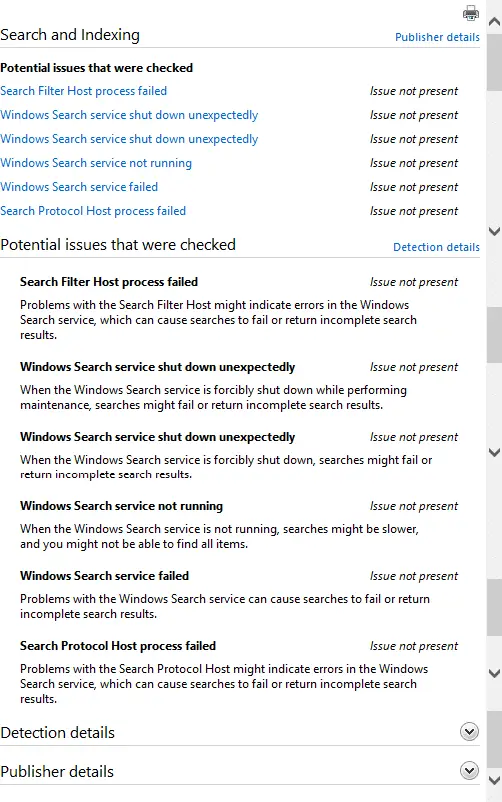
The Search and Indexing troubleshooter checks for the following potential issues:
- Search Filter Host process failed: Problems with the Search Filter Host might indicate errors in the Windows Search service, which can cause searches to fail or return incomplete search results.
- Windows Search service shut down unexpectedly: When the Windows Search service is forcibly shut down while performing maintenance, searches might fail or return incomplete search results.
- Windows Search service shut down unexpectedly: When the Windows Search service is forcibly shut down, searches might fail or return incomplete search results.
- Windows Search service not running: When the Windows Search service is not running, searches might be slower, and you might not be able to find all items.
- Windows Search service failed: Problems with the Windows Search service can cause searches to fail or return incomplete search results.
- Search Protocol Host process failed: Problems with the Search Protocol Host might indicate errors in the Windows Search service, which can cause searches to fail or return incomplete search results.
If necessary, the troubleshooter fixes the NTFS permissions for the Windows Search data folder so that the NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM account has the required permissions. By default, the search data folder is located at %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\. The troubleshooter can also reset the Windows Search settings and force a rebuild of the Search index if deemed necessary.
Manually Reset Windows Search and Rebuild the Index
The Search troubleshooter is the most preferred way to troubleshoot search and indexing issues, as it automates many things (depending upon the checkbox options you selected).
However, if you want to manually reset Windows Search, delete and rebuild the index, use these steps:
- Start the Registry Editor
regedit.exeand go to:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search
- Change the registry value
SetupCompletedSuccessfullydata from1to0
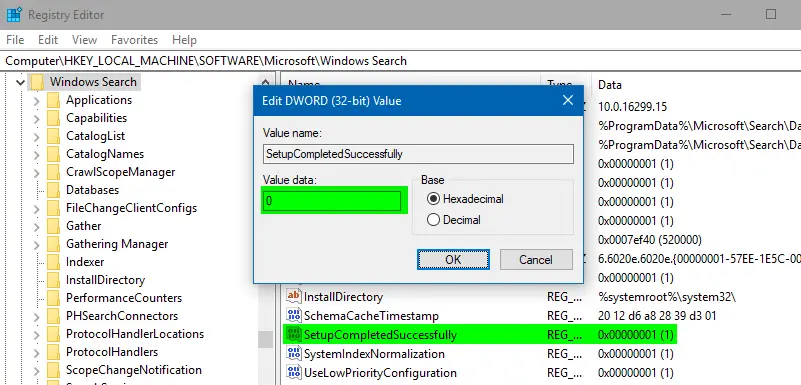
The above registry change SetupCompletedSuccessfully = 0 causes Windows Search to clear custom indexed locations, add default locations, and rebuild the index from scratch. - Exit the Registry Editor.
- Open the Services MMC (
services.msc) - Restart the Windows Search service.
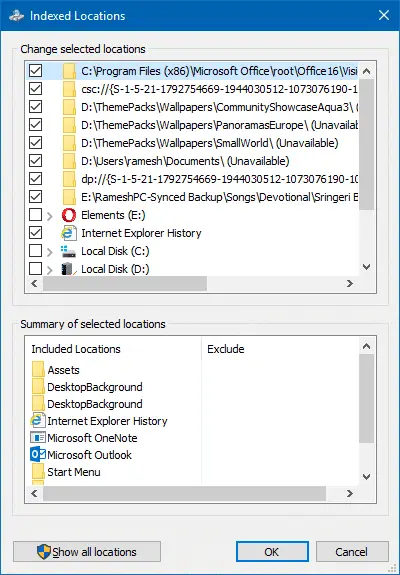
Before resetting search, this is how the Indexed Locations dialog looked like, containing many obsolete folder locations:
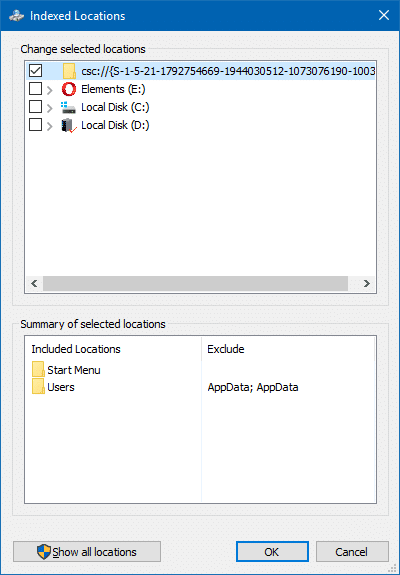
After resetting the search, Included Locations is reset to Windows 10 defaults.
This reset & rebuild method essentially resolves most of the Windows search problems.
Reset & Rebuild Search Index using command-line or batch file
To accomplish the above steps using the command-line/batch file, follow the steps:
- Copy the following contents to Notepad, and save the file as
reset_rebuild_search.batsc config wsearch start= disabled net stop wsearch REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search" /v SetupCompletedSuccessfully /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f del "%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.edb" del "%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.db" :wsearch sc config wsearch start= delayed-auto net start wsearch IF NOT %ERRORLEVEL%==0 (goto :wsearch) ELSE goto :END :END
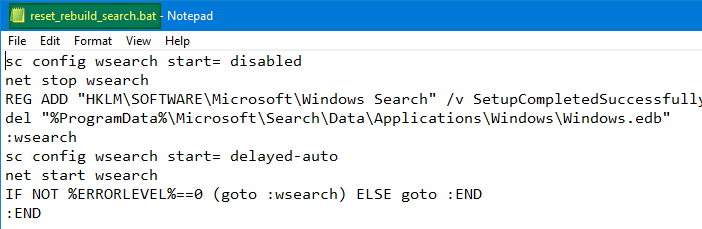
- Right-click
reset_rebuild_search.batand click Run as administrator. This runs the batch file under elevated (administrator) rights.
Note: The Windows.edb file doesn’t exist in Windows 11. Instead, Windows 11 uses Windows.db which is an SQLite database file.
This resets the search locations to default settings and rebuilds the search index from scratch.
Rebuild Windows Search Index Without Resetting
The earlier method resets Windows Search locations and forces a rebuild of the index upon the next restart, or after restarting the Windows Search service. To rebuild just the index without resetting the indexed folder locations, use these steps:
Click Start, type indexing, and click on Indexing Options in search results.
In case the Start menu search doesn’t work, you can launch Indexing Options directly by running the following command from Run dialog or Command Prompt.
control srchadmin.dll
In the Indexing Options dialog, click Advanced. Under Troubleshooting section, click Rebuild.
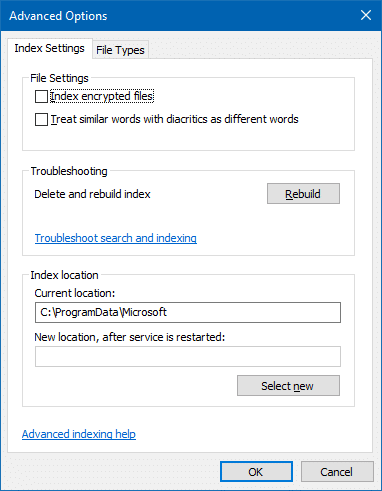
This deletes and rebuilds the index completely.
Note that if Windows detects user activity in the system, indexing is slowed down drastically. After a couple of minutes of no user activity, indexing continues in full swing. Regardless, when I checked, the searchindexer.exe and its allied processes didn’t use more than 15% of the CPU at any given point in time, even when the system was left idle.
Rebuild Search Index using Batch file (without resetting the locations)
- Copy the following contents to Notepad, and save the file as
reset_search.batsc config wsearch start= disabled net stop search del "%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.edb" del "%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.db" :wsearch sc config wsearch start= delayed-auto net start wsearch IF NOT %ERRORLEVEL%==0 (goto :wsearch) ELSE goto :END :END
Note: Windows.db is present in Windows 11. Windows.edb is for Windows 10.
- Right-click
reset_search.batand click Run as administrator.
The above batch file rebuilds the search index from scratch. It doesn’t reset the search index locations list, though.
Defrag the Search index database Windows.edb to reduce the file size
If you index too many files & folders and the Outlook PST files, the Windows search index database file Windows.edb would grow huge in size. In some instances, the file size can be larger than 50 GB. That’s because, in Windows 8 and Windows 10, both properties and persistent indexes are stored in Windows.edb. Also, Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10 index the entire contents of files, regardless of their size.
Important: The procedure works only in Windows 10. On Windows 11, there is no longer a Windows.edb JET database file. Windows 11 uses Windows.db, which is a SQLite Database file that can’t be compressed using esentUtl.exe.
To reduce the Windows search index database size, index less content. Another option to reduce the size of Windows.edb is to compact or defrag the file using esentutl.exe. Follow these steps:
Open an admin Command Prompt window, and run these commands:
sc config wsearch start= disabled net stop wsearch esentUtl.exe /d %AllUsersProfile%\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\Windows.edb sc config wsearch start= delayed-auto net start wsearch
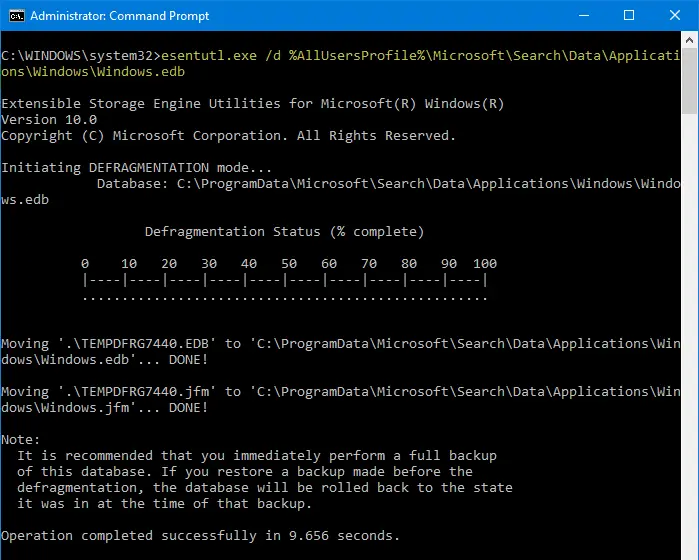
The above commands stop/disable Windows Search, compact (defrag) the search index database, and then start Windows Search. Compaction of the Windows.edb database has reduced the size to 200 MB from 310 MB on my computer — ~30% savings.
Resetting the Search index, or removing unwanted folder locations from the search index, and compacting the database would certainly improve the search performance in your system.
One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
One "tiny" share from you would seriously help a lot with the growth of this blog. Some great suggestions:- Pin it!
- Share it to your favorite blog + Facebook, Reddit
- Tweet it!
FINALLY
This should not be this hard to do but it is for some reason.
This is the only thing that worked for me. Windows is so f’ed up, they don’t even know what’s in their software.
Thank you!!!
Check out this quote from a help forum:
“Come on Microsoft! What are you thinking? Is there anyone home?”
You can also open a Admin CMD prompt and run this command.
rundll32.exe shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL srchadmin.dll
Can someone help with the following.
In Windows 10 ( also in other versions ) Right Click your HDD and go to Properties.
Then Un Tick ( Allow files on this drive to have contents indexed in addition to file properties ).
The next step you have to agree to.
Now this Takes some Time to go through and Remove the Indexing.
One might Ask Why I want to do this, well Trust me it has it’s Advantages.
Anyway I am looking for a way to do this in the ISO.
So as that When the Installation of Windows is Complete that That Item Is Already Un ticked or Not Used.
That would Save a lot of Time after an Install.
I normally Use Nlite for Slipstreaming my ISO’s to get them Up to Date..
I can’t find anything in Nlite that would Disable Indexing.
I have tried Disabling Windows Search in Services, but that does not do it.
Any help would be appreciated
This worked perfectly fine! Thanks a lot!
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Search
Change the registry value SetupCompletedSuccessfully data from 1 to 0
That does not work for me. When I follow those directions it shows :
Default REG_SZ (value not set)
Great – this worked for me in that it got the search re-indexing which when I tried to do it before (but without the registry edit bit) it did nothing much.
Thanks
I did not work for me. I tried it several times, I followed every step but the Search button won’t open 🙁
Congrats for this amazing post!
I have a question about Windows.edb defragmentation.
You said: “To reduce the Windows search index database size, index less content.”
Does it mean that the defragmentation remove the “content” part of the database?
Best,
@Phil: esentUtl compacts/defrags the database file. It doesn’t remove the content part.