When you try to upload a video on Twitter, error “Your media file could not be processed” may be displayed during the processing stage. Twitter lists out the specifications for media files on their support site. If your media file doesn’t fit into their technical specifications, the error appears.
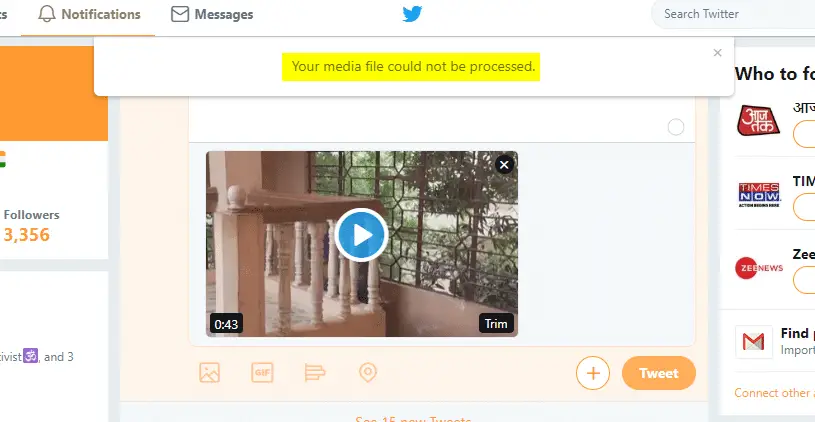
This post tells you how to resolve the problem.
What type of videos does Twitter support?
According to Twitter, your video file needs to match the following specs:
- Minimum resolution: 32 x 32
- Maximum resolution: 1920 x 1200 (and 1200 x 1900)
- Aspect ratios: 1:2.39 – 2.39:1 range (inclusive)
- Maximum frame rate: 40 fps
- Maximum bitrate: 25 Mbps
Twitter currently supports MP4 and MOV video formats on mobile apps. On the web, Twitter supports the MP4 video format with H264 video encoding and AAC audio encoding. Videos up to 512MB can be uploaded. However, you will be prompted to edit videos to 2 minutes and 20 seconds or less in length.
Fix “Your media file could not be processed” Error
To fix the “Your media file could not be processed” error when uploading a video on Twitter, the media file must be converted or encoded in the right format. Follow one of these methods:
Option 1: Using Handbrake GUI
Handbrake is a 3rd party application that converts video from nearly any format to a selection of modern, widely supported codecs. Using Handbrake you can turn or encode any video so that it becomes compliant with Twitter’s specifications.
- Download Handbrake and run it.
- Open the video file in Handbrake.
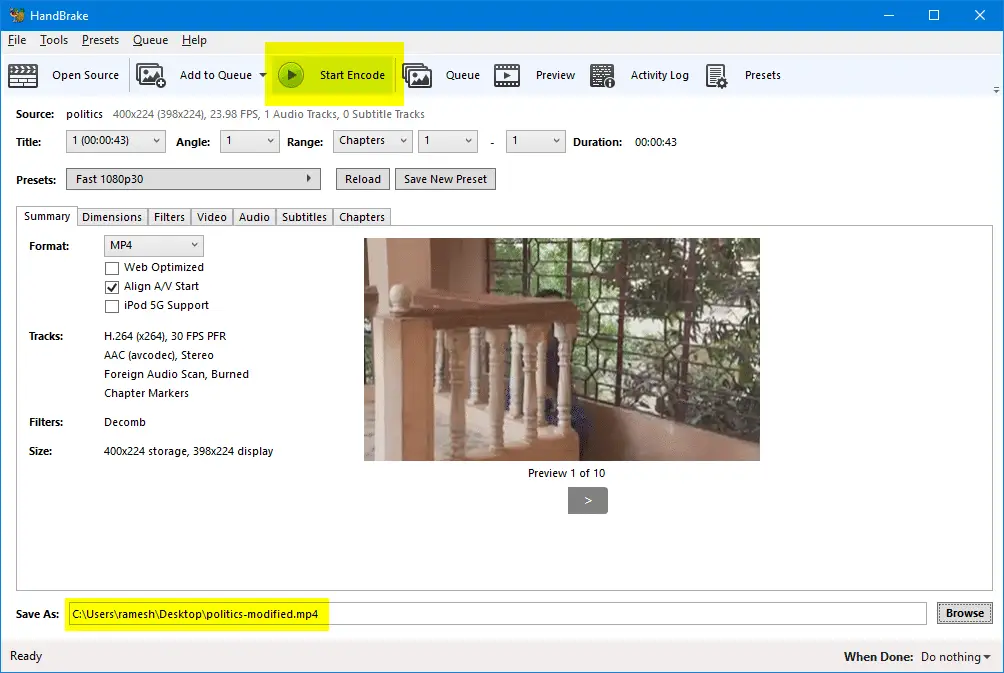
- In the Save As: field, mention the path and filename for the file you’re going to modify. Leave the default settings and Presets as they are.
- Click
Start Encode. The encoded file is now saved to the chosen location. See if you can upload it on Twitter.
You should have noticed an option (checkbox) named Web Optimized in the Handbrake user interface. Web Optimized option for the MP4 container, if enabled, moves some of the video metadata from the end to the beginning of the final video file. As Handbrake documentation describes, this option is mostly useful for streaming on the internet. As far as the Twitter error is concerned, enabling Web Optimized setting is optional.
![]() The default preset
The default preset Fast 1080p30 should be fine for most users. If you want to reduce the output file size, you can change the desired preset. Alternately, you can choose Fast 1080p30 but customize the settings manually — i.e., lower the bitrate or adjust the CRF slider in the Video tab, or reduce the bitrate for the audio track via the Audio tab.
Preset: Fast 1080p30 Type: MP4 Video: H.264 Framerate: 30 FPS (peak) Constant rate factor (CRF): 22 Audio: AAC (Stereo) Audio bitrate: 160 Kbps (Constant) Encoding Speed: Fast File Size: Average
For a full list of presets, check out HandBrake Documentation — Official presets.
Option 2: Handbrake Command-line interface (CLI) tool
Handbrake also has a command-line version of the tool if you need to bulk encode media files with the Windows batch file or script. Download HandBrakeCLI and extract the contents to a folder.
Use the following syntax to encode a file:
handbrakecli.exe -i "source_file_name" -o "target_file_name"
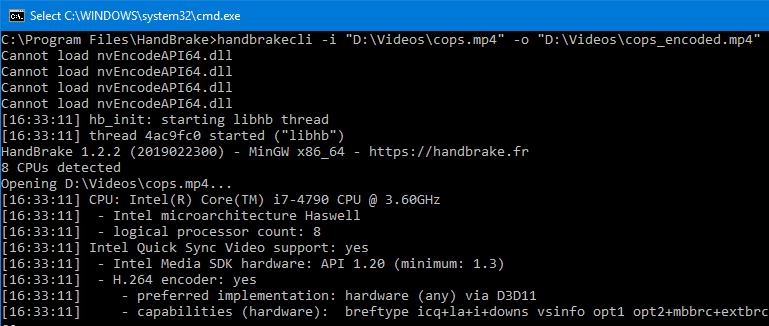
The above command will encode with the default “Normal” Preset (Fast 1080p30). If you want to encode with customized bitrate, framerate, and other settings, etc., refer to the (Official) HandBrake Documentation — CLI Options.
Option 3: Using FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a free and open-source project consisting of a software suite of libraries and programs for handling video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. You can do pretty much any media conversion/encoding task using this console tool. There are many third-party programs such as Screen to Gif, File Converter, etc. that are bundled with FFmpeg.exe. [Download FFmpeg]
To fix the “Your media file could not be processed.” error for a media file, reencode the video (and audio) using FFmpeg.exe. To do so, use the following command-line syntax:
ffmpeg -i input_file output_file
Examples:
ffmpeg -i input.mkv output.mp4 ffmpeg -i input.mp4 output.mp4
When you run the above command-line, the input video is reencoded with H264 format with AAC audio and saved to a file in MP4 video format. If the input audio stream is in dash or any other format, FFmpeg converts it to AAC – M4A by default.
Before encoding:
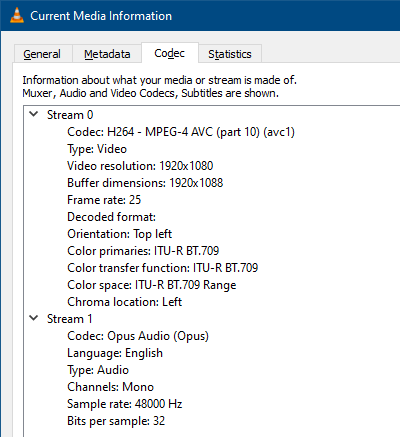
After encoding:
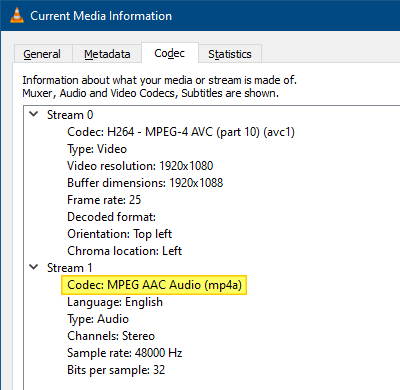
This makes the media file compatible with Twitter, assuming that the other requirements are met. You should now be able to upload the encoded video on Twitter without getting the error “Your media file could not be processed.”
One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
One "tiny" share from you would seriously help a lot with the growth of this blog. Some great suggestions:- Pin it!
- Share it to your favorite blog + Facebook, Reddit
- Tweet it!
Hello,
thanks for sharing.
Can I ask you a question?
After I download this app and upload video, click “Strat Encode” and it will shown: “The output directory you have chosen eiter does not exist, or you do not have permissions to write files to it.”
What’s the reason for that?
Thanks for your help
@scarlett: Which directory you’re using for output? Can you set Desktop as the output directory to see if that works?
If you’re using Windows Defender, see if adding handbrake’s executable to the CFA whitelist helps.
Still unable to upload video after following your steps 🙁
@Kevo: Can you send me a sample video that you can’t upload to Twitter?
After following the steps, when I go through Twitter and try to upload the post, Twitter does not seem to recognize the Handbrake encoded file – any tips?
It worked for me! Thank you!
There are presets for handbrake. You can encode for a huge variety from 4k-video very low-quality.
It would be helpful to include the settings necessary to upload it on twitter.
@titule: The default preset Fast 1080p30 itself works well. As long as you use H264 and AAC codecs, it’s fine. If you need to alter the quality (RF) or bitrate from a preset, you can do so via the Audio or Video tab.
Thank you – I got my video uploaded on twitter.
Hi Ramesh, I tried the ffmpeg approach but I still get the same error.
My video details:
resolution/aspect ratio: 1920×804 (2.38806:1)
size: 21.4MB
frame rate: 24
codec: H264 – MPEG-4 AVC
no audio track
output of ffmpeg -i:
Input #0, mov,mp4,m4a,3gp,3g2,mj2, from ‘.\scifi_city_1920x804.mp4’:
Metadata:
major_brand : isom
minor_version : 512
compatible_brands: isomiso2avc1mp41
encoder : Lavf58.78.100
Duration: 00:00:10.33, start: 0.000000, bitrate: 17389 kb/s
Stream #0:0(und): Video: h264 (High 4:2:2) (avc1 / 0x31637661), yuv422p(tv, bt470bg/unknown/unknown), 1920×804, 17388 kb/s, 24 fps, 24 tbr, 500k tbn, 48 tbc (default)
Metadata:
handler_name : VideoHandler
vendor_id : [0][0][0][0]
@Mat: Can I get that video file (in case it’s for public access)? Meanwhile, pls try Handbrake or Handbrake CLI. Handbrake has always worked for me.
Thank u serrr, it’s work tested by me!
I Love your tutorials, thanks bro