Safe mode starts Windows in a basic state, using a limited set of files, drivers, and services. If a problem doesn’t happen in safe mode, this means that default settings and basic device drivers aren’t causing the issue.
There are other situations that warrant booting Windows into Safe Mode — e.g., fixing the service registry settings, writing to certain protected directories or registry locations, deleting a stubborn file or folder, or logging in as built-in Administrator, etc. — which are otherwise not possible (“Access is denied” or “File in use”) when in Normal mode.
In this article, we’ll see how to start your Windows 10 or 11 computer into Safe mode.
Start Windows 11 or 10 in Safe Mode
Option 1
- Click Start, click on the Power button, press and hold the Shift key down and click Restart. This starts the Windows Recovery Environment.
Alternatively, you can restart your device into safe mode from the Windows sign-in screen. On the Windows sign-in screen, press and hold the Shift key while you select Power → Restart. See also How to access Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
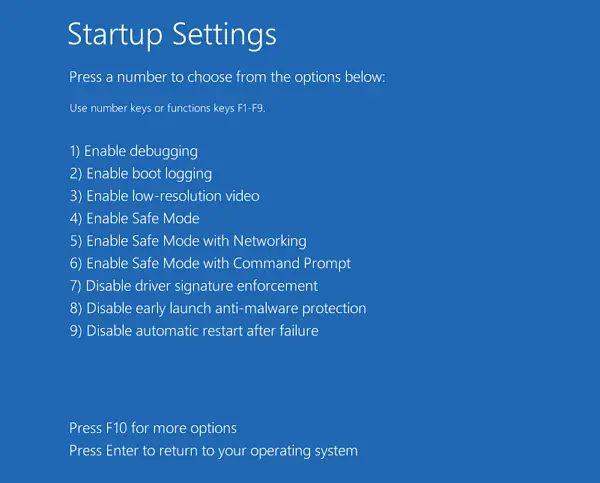
- In Windows RE, click Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Startup Settings.
.png)
.png)
.png)
- In Startup Settings, press the 4 or F4 button on your keyboard. Or, to start Windows in “Safe Mode with Networking”, press 5 or F5.
- Windows 10/11 will now restart in Safe Mode.
![]() The built-in “Administrator” account shows up on the lock screen while in Safe Mode if no other administrator account user exists on the computer. This is regardless of whether the built-in Administrator is currently enabled (active) or not.
The built-in “Administrator” account shows up on the lock screen while in Safe Mode if no other administrator account user exists on the computer. This is regardless of whether the built-in Administrator is currently enabled (active) or not.
Option 2: Using MSCONFIG
The following steps force Windows to start into Safe mode every time you reboot the device.
- Launch the System Configuration utility by running msconfig.exe.
- Select the Boot tab.
- Select the Safe Boot option and click Apply.
- Choose Restart to apply the changes when the System Configuration window pops up.
Important: After you finish your troubleshooting using Safe Mode, launch msconfig.exe again and undo the Safe Boot option. Or else, Windows will default to Safe mode on every reboot.
See also: Windows Defaults to Safe Mode, Can’t Boot into Normal Mode.
One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
One "tiny" share from you would seriously help a lot with the growth of this blog. Some great suggestions:- Pin it!
- Share it to your favorite blog + Facebook, Reddit
- Tweet it!