You probably know how to add or remove environment variables using GUI in Windows. It can be done by launching sysdm.cpl → Advanced → Environment Variables. Alternatively, one can run the following command in the Run dialog to launch the Environment Variables dialog directly:
rundll32 sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables
(To set per-system environment variables, the above command needs to be run from admin Command Prompt.)
This post tells you how to use the Setx command to add a user environment variable.
Setting User Environment Variable
Open a Command Prompt window and type SETX /? to know the command usage. For example, to set the JAVA_HOME variable, you would use:
SETX JAVA_HOME "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_02"
(Depending upon the version of the JDK installed and the bitness of your OS, change the JDK folder path accordingly.)
This permanently sets the environment variable for your user account; It takes effect for future Command Prompt windows.
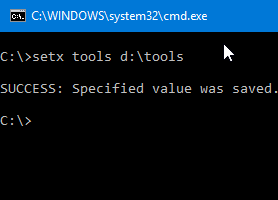
Delete a User Environment Variable
To clear the user variable, use this syntax/example:
SETX JAVA_HOME ""
This, however, doesn’t delete the value from the following registry key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment
So you need another command to clear it, although this is optional.
REG DELETE HKCU\Environment /V JAVA_HOME /F
This clears the JAVA_HOME user variable.
Note: The Setx command can also be used to set System Environment Variables using the “/M” switch, but you need to run it from elevated or administrator Command Prompt.
One small request: If you liked this post, please share this?
One "tiny" share from you would seriously help a lot with the growth of this blog. Some great suggestions:- Pin it!
- Share it to your favorite blog + Facebook, Reddit
- Tweet it!
Thanks für this post!
Found an article about this for german users:
itnator.net/setx-parameter-environment-variablen/
Sabine
THANKS !
i needed this info ,though i`m still looking for like a more complete pdf usage kind to setx path “%path% , them paths are my nightmare at times. thanks again